Shield Report 2006; A surveillance scheme of occupational asthma in the Midlands |

|
S Manney, V Moore, AS Robertson, MS Jaakkola, AD Vellore and PS Burge. Occupational Lung Disease Unit, Heartlands Hospital, Bordesley Green East, Birmingham B9 5SS
SHIELD is the Midland Thoracic Society’s Surveillance Scheme for Occupational Asthma for the West Midlands. The scheme, which was set up in January 1989, was established to study the general and specific incidence of occupational asthma within the West Midlands region and Metropolitan County. There were problems with the parent MTS rare disease reporting scheme in 2003 due to data protection issues which has limited reports from outside the Birmingham Chest Clinic. Despite this, the rate of reporting has shown little change over the years, but increased sharply in 2004, mainly due to a major outbreak, and has returned to slightly lower levels this year. Fifty-seven reports have been received so far for 2006. The data protection issues are now being resolved and it is hoped that reporting from other hospitals will be implemented this year (2007).
The most common joint cause in 2006 was Metal Working Fluid (15.8%) and Isocyanates (15.8%). Biocides and cleaning agents came third at 10.5%. Latex has continued to decline, both in percentage terms and numbers (1 person, 1.8%), suggesting that substitution of latex gloves is continuing.
96.5% of cases reported in 2006 were by the Birmingham Chest Clinic and 3.5% by others. We hope to increase the number notified by others this year now that data protection issues have been resolved. The most common method for the diagnosis of occupational asthma still remains a history of improvement of symptoms during holidays or periods off work. Some form of objective confirmation was sought in 78.9% of patients.
We still have plans for web based reporting, but there are higher priorities on the agenda and the plans remain on the shelf for the time being.
Introduction
Shield is a joint project between the West Midlands branch of the Society of Occupational Medicine and the Midland Thoracic Society. The scheme, which was set up in January 1989, was established to meet three main objectives. 1) To study the general and specific incidence of occupational asthma within a defined geographic area, 2) To determine proposed mechanisms of asthma, and 3) to audit diagnostic methods and objectives. Chest physicians and members of the West Midlands Group of the Society of Occupational Medicine implemented the scheme, by reporting each new case using a questionnaire format. The questionnaire covers confidential personal information on the patient, details of the diagnosis, information about their occupational history, and the outcome after diagnosis.
The last report on Shields progress was written in 2005 and summarised the information gained in that year, to that of previous years, 2004 and 2003. This report aims to update the participants of Shield by summarising the trends found in 2006 compared to those found in 2005 and 2004.
Outbreak of the year
This year we have discovered an outbreak of occupational asthma as well as other work related symptoms in a school for children with special needs. We have seen 8 workers this year which followed on from 6 seen in 2005. The school itself employs around 110 workers. The cause of this outbreak is as yet to be confirmed, but possibilities include flooring adhesive and cleaning products.
Agent Awareness
The main agent reported to the scheme in 2004, 2005 and 2006 was metal working fluid, joined in 2006 by isocyanates, which had been in second place for 2004 and 2005. This is mainly found in industries that grind and drill metal components. The West Midlands is an area of major metal working and metal-working fluids have been a regular cause of occupational asthma since Shield began. In the past most cases have been due to inhalation of used oils, where microbial contamination is the most likely cause. In one plant, cobalt (from stellite welding) dissolved in the coolant is the most common cause. Occasional cases are due to constituents of the unused oil, particularly colophony or tall oil products. We have also had a previous outbreak of alveolitis and asthma due to a contaminated water-based humidifier in a printing works, controlled by replacement with a steam humidifier (Thorax 1985;40: 248-254).
Shield Data
Number of Cases
The number of cases of occupational asthma reported to the Shield scheme is 57 so far. When the SHIELD report for 2005 was written, there were 78 cases notified, but now this figure is up to 88. It is difficult to compare notification for each year properly, as the last few years are likely to change, therefore the graph below is only as a guideline.
Figure 1 Number of cases diagnosed with occupational asthma between the years of 1980 and 2006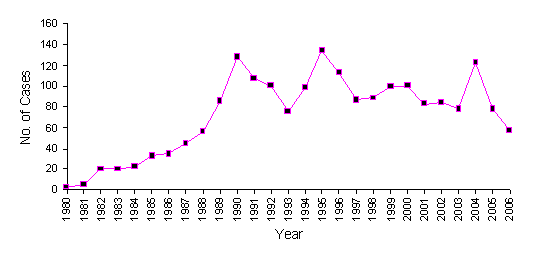
Personal details
In the year of 2006, 57 new cases have been reported to the scheme so far. There were 33 males (57.9 %), and 24 females (42.1 %). 47 (82.5%) of the new cases had no pre-existing asthma, and 32 (56.1%) had never smoked.
Reporting Hospital and Physician
The Shield scheme is confined to the West Midlands Region and the West Midlands Metropolitan County. In this region there are many chest physicians, hospitals, clinics and other organisations, which are known to the Shield scheme. However, many of these have not been asked to report over the last year due to the data protection issues. Therefore, in 2006, 55 (98.2 %) of the cases reported to Shield were through the Birmingham Chest Clinic, and 2 (3.5 %) through other organisations. We are hoping that there will be more cases reported from other institutions in the coming year.
Suspected agents at work
In 2006 the reported agents that the workers were exposed to was a heterogenous mix, and was not dominated by the outbreak. The most common in 2005 was metal working fluid due to an outbreak seen in that year, as was also the case in 2004, but in previous years (except 1997) the most common was isocyanates. Reports for isocyanates this year are equivalent to those for metal working fluids. 419 cases of isocyanate suspected asthma have now been reported to the scheme, the first case being in 1978. 12 cases of isocyanate asthma were diagnosed in 2005 and 25 cases in 2004. Latex cases are continuing to decrease and in the last 2 years only 4 notifications have been made. Only 1 chrome case was noted this year, which shows a marked decline from previous years.
The top five agents reported in 2006 were;
- Metal Working Fluid 15.8% 19 cases
- Isocyanates 15.8% 19 cases
- Biocides/Cleaning agents 10.5% 16 cases
- Carpets 18.8% 5 cases
- Flour 17.0% 4 cases
Figure 2 Comparison of the percentage of patients exposed to the top five agents in 2006 to those exposed in 2005-2002.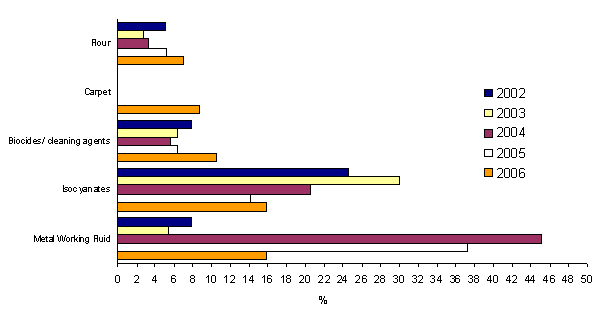
Employers and Jobs
There were 48 different employers reported to the scheme in 2006. 36 of these were new to the scheme. The major outbreak for 2006 currently accounts for 14.0% of all reports in 2006.
Around 49 different jobs were reported in 2006, although it would be possible to group some of the specific jobs into broader categories (e.g. teachers). The most common job was teachers at 17.5% of all notifications in 2006.
Table 1 A list of the most common agents reported in 2005 with the corresponding jobs
| Agent Exposed |
Job |
| Metal Working Fluid |
Production manager, machinist, electrician KV6, setter, works manager (grinding), OP 90 worker, old reducing operative, engineer, Central manager MWF, CNC operator |
| Isocyanates |
Boat builder, coach builder, technical director, teacher (car repairs), caster, body-2-white (build technician), paint sprayer |
| Biocides/Cleaning agents |
Reprographic manager, teacher, housekeeper, cleaner, nurse |
| Carpet |
Head teacher (No 2), Teacher (support worker), Teacher (home economics), teaching assistant, teacher |
| Flour |
Production supervisor, pastry maker, pastry cook, sales assistant in bakery |
| Wood dusts |
Boat builder, coach builder, design and technology teacher |
| Welding fume |
Boat builder, welder, works manager (grinder and welder) |
| Adhesive |
Sewer, cable assembler |
| Chrome |
No job given |
Methods used for diagnosis
The methods used for the diagnosis that are documented on the shield form are; 1) Improvement on holiday, 2) Improvement off work, 3) Serial peak flow charts, 4) Specific IgE, 5) Methacholine at work, and 6) Methacholine away from work and 7) Specific bronchial provocation tests. 48 cases were documented as improving off work and on holidays. Of these, 44 cases had at least one other investigation. The most common investigation was serial peak flow charts (38 cases) followed by specific IgE (21 cases). There were 19 specific challenges performed in 2006, but only 6 of these were on patients diagnosed in 2006.
Table 2 Percentage use of each method of diagnosing occupational asthma in 2006, 2005 and 2004.
| Method |
% 2006 |
% 2005 |
% 2004 |
| Improving on holidays |
93 |
86 |
92 |
| Improving off work |
82 |
91 |
87 |
| Serial peak flow |
67 |
86 |
78 |
| Specific IgE |
37 |
60 |
66 |
| Methacholine at work |
46 |
50 |
53 |
| Methacholine away from work |
26 |
26 |
18 |
Specific Bronchial Challenge
(positive challenges) |
7
(3.5) |
10
(8) |
8
(5.5) |
Proposed method of asthma
Figure 4 shows the proposed mechanism of asthma in patients with diagnosed occupational asthma in 2006, 2005 and 2004. In 2006 the most commonly reported mechanisms of asthma were allergic (56 %) and unknown (30 %). In 2005 an allergic and unknown mechanisms were also reported in most cases (41% and 49% respectively). The percentage of ‘no answer’ has risen slightly in 2006 to 12% from an average of the past couple of years of 8% remained similar in the last 3 years at an average of 8%. The other mechanisms (irritant and direct pharmacological effect) still remain very low in the percentage of proposed mechanisms 1.8 and 0% respectively).
Figure 3 Proposed mechanisms of asthma in 2006, 2005 and 2004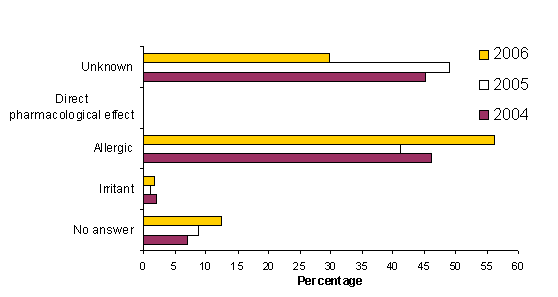
Subsequent History
The subsequent history of the patients diagnosed with occupational asthma in 2006 has a similar amount of workers remaining exposed or moving within the same workplace. The number off sick has risen slightly this year, and the amount who have had the agent removed at work has decreased again. The outbreak in 2004 had a large influence on the agent removal figures however. This is probably less likely to happen where only one or two workers are having problems in a workplace. Relocation at work probably remains the most effective solution in most cases. The recorded subsequent history of the patient is taken at diagnosis and is subject to change so these figures will change with time.
Figure 4 Subsequent history of patients diagnosed of occupational asthma in 2006, 2005 and 2004 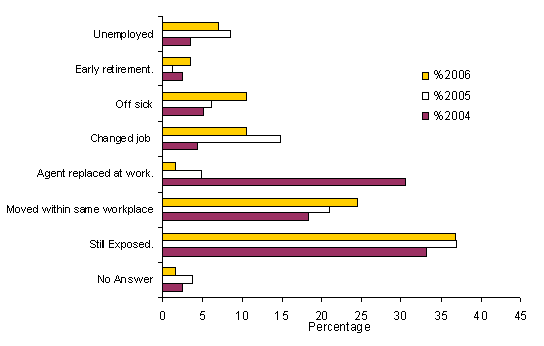
Gold Standards
A gold standard occupational asthma case is defined by either; 1) Bronchial challenge test, 2) A four fold change in their bronchial reactivity with a good history, or 3) Positive IgE with a good history, and all of these can be accompanied by a good quality PEF record. 3.5% of cases have become gold standards in 2006 so far.
Future Developments
The problems with the Shield scheme are lack of reporting, a need for constant updating and a lack of resources. We have solved the data protection issues and will start to request notifications from other institutions this year. We would like to add web based reporting to improve notification and updating but this is on hold for the time being due to time constraints. There are organisational and technical changes to be made to improve accuracy and to help keep data up to date. We have plans for these but there is no date set for implementation as yet. The development of a better internet site for the Midlands Thoracic Society this year should help.
Conclusions
Occupational asthma remains a serious disease causing much morbidity, and is potentially preventable. The Health and Safety Executive are currently emphasising the need to control occupational asthma. Workers in schools are among those who have been most reported this year and should be studied to assess the development of occupational asthma.
Comments
Please sign in or register to add your thoughts.